Classification of Joints
The majority of joints in cabinet work are very old, and were designed years ago to perform certain duties. From experience their properties have become standard in order to maintain a maximum of strength with pieces they connect.
Joints used in cabinet work may be classified into three main groups:
- Widening joints
- Angle joints
- Framing joints
Widening joints
The members are joined edge to edge
- Used to produce wide boards from a number of narrow boards.
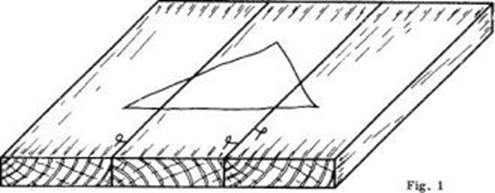
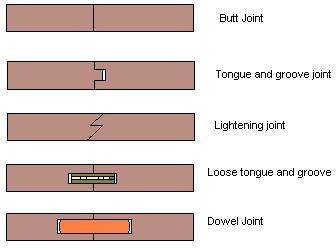
Uses: table tops, floor boards,- Angle joints (box-like construction)
The members are joined end to face or have their faces at right angles and have their edges flush
- Used in box-like construction such as solid cabinets, boxes, drawers
- With the introduction of manufactured boards such as particleboard and MDF angle joints have become more prevalent.

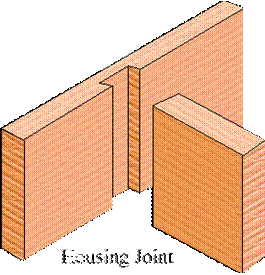

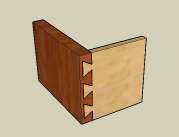
 Dovetail joints
Dovetail joints
Framing joints
The members are joined end to edge, with their edges at right angles.
 Used in frame-like construction such as panelled doors, tables, chairs, picture frames, window sashes
Used in frame-like construction such as panelled doors, tables, chairs, picture frames, window sashes
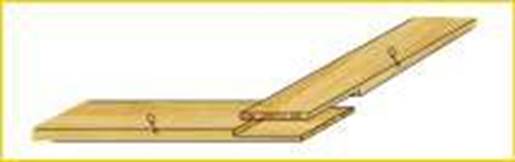
Half lap joints

Mortise and tenon joints
Bridle joints
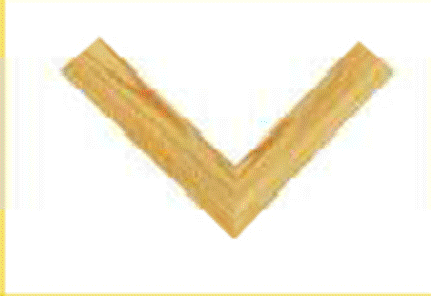
Mitre joints