 |
Official name: Socialist Republic of Vietnam Size: 127,881 square miles (331,210 square kilometers); slightly larger than New Mexico Population: 91,519,289 as of 2011 Capital: Hanoi Official language: Vietnamese, though English is widely spoken Currency: Dong
|
Fast Facts
Official Name: Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Form of Government: Socialist republic
Capital: Hanoi
Population: 84,402,966
Official Language: Vietnamese
Money: Dong
Area: 329,247 sq km

Rice Paddies

Hanoi

Fruit Vendor
Major Mountain Range: Annam Cordillera
Major Rivers: Mekong, Red, Ma, Perfume
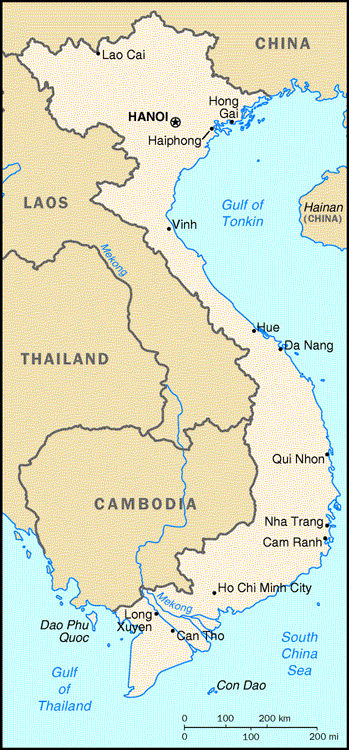
Two of Vietnam's largest rivers, the Mekong in the south and the Red in the north, end at the South China Sea in huge swampy plains called deltas. These regions are home to most of the country's people and provide fertile ground to grow rice and many other crops.
Nature
Vietnam's mountainous terrain, forests, wetlands, and long coastline contain many different habitats that support a great variety of wildlife. Some 270 types of mammals, 180 reptiles, 80 amphibians, and 800 bird species reside in Vietnam.
Many rare and unusual animals live in Vietnam, including giant catfish, Indochinese tigers, Saola antelopes, and Sumatran rhinos. The government has set up 30 parks and reserves to protect its animals, but their survival is in doubt because much of their habitat has been cleared for lumber or to grow crops.
Vegetation
Tropical forests once covered most of Vietnam, but over the past few hundred years, logging has reduced the forest cover to only about 19 percent. The government has launched a replanting program in an attempt to restore these woodlands.
History
Vietnam's first civilizations arose in the Red River Valley some 5,000 years ago. These northern tribes flourished until 207 B.C., when their region was conquered by a Chinese lord, who established a kingdom called Nam Viet. (Vietnam).
In 111 B.C., Nam Viet became part of the Chinese empire, which ruled the north until A.D. 939, when a Vietnamese commander named Ngo Quyen organized a revolt that drove the Chinese out. Later dynasties renamed the country Dai Viet and gradually extended their territory south.
By the mid-1500s, Dai Viet was divided between rival kingdoms: the Trinh in the north and the Nguyen in the south. In 1802, a Nguyen lord, with the help of the French, defeated the Trinh and renamed the country Vietnam.
By 1890, however, France had taken over Vietnam. Japan took control briefly during World War II, and when the war ended with Japan's defeat in 1945, Ho Chi Minh, the leader of the Vietnamese Communist Party, declared Vietnam an independent nation.
French attempts to retake Vietnam led to war with the communist Vietnamese, called Viet Minh. Fighting ended in 1954 with the partition of the country into communist North and non-communist South Vietnam.
In 1957, communist rebels in the south, called Viet Cong, rose up. War between the North and South ensued, and other countries, including the United States, Russia, and China, soon became involved. The fighting lasted until 1975, when the communists overran the south and took its capital, Saigon.
People & Culture
Most Vietnamese people live in the countryside, mainly in the river delta regions of the north and south. Recently though, people have begun to move to the main cities of Ho Chi Minh (formerly Saigon) and Hanoi.
The most popular sports in Vietnam include soccer, table tennis, volleyball, and martial arts. Vietnamese food is a blend of Chinese and Thai styles and features seafood and homegrown fruits and vegetables.
As a communist country, Vietnam has no official religion. But people are free to worship if they want to, and many follow what's called the "Three Teachings" of Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism.
Government & Economy
Vietnam is a socialist state governed by the Communist Party of Vietnam. A president, chosen by the National Assembly, is head of state and commander of the armed forces. An appointed prime minister runs the government.
Vietnam's main exports include crude oil, seafood, rice, shoes, rubber electronic, coffee, and clothing. Between 1975 and the late 1980s, Vietnam traded mainly with other communist countries, but since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1990, it has expanded trade with other nations.